Leetcode 0199. Binary Tree Right Side View
199. Binary Tree Right Side View
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]
Explanation:
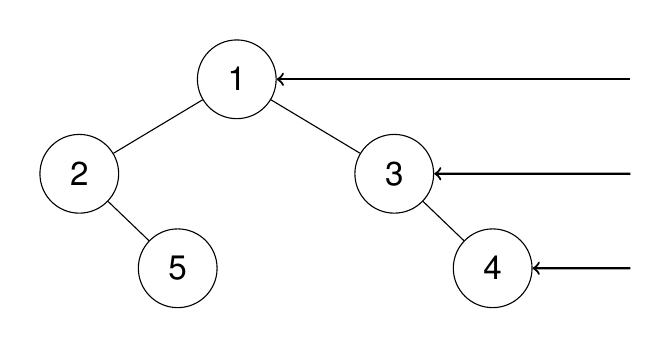
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5]
Output: [1,3,4,5]
Explanation:

Example 3:
Input: root = [1,null,3]
Output: [1,3]
Example 4:
Input: root = []
Output: []
题目大意
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root,想象自己站在树的右侧,返回从顶部到底部能看到的节点值。核心是:每一层只保留「最右侧」的一个节点值,按层从上到下排列。
例如:
- 输入二叉树
[1,2,3,null,5,null,4],右视图为[1,3,4](第一层最右是 1,第二层最右是 3,第三层最右是 4)。
解题思路
这种实现的核心思想是利用深度优先搜索(DFS),但改变了访问顺序:
- 先递归访问右子树,再递归访问左子树
- 记录当前遍历的深度,当某个深度是第一次到达时,当前节点就是该深度从右侧能看到的节点
- 用结果数组的大小来跟踪已经记录的深度,当深度等于结果数组大小时,说明是首次到达该深度
代码实现
1 | /** |
All articles on this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless otherwise stated.

