Given the head of a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
Example 1:
1
2
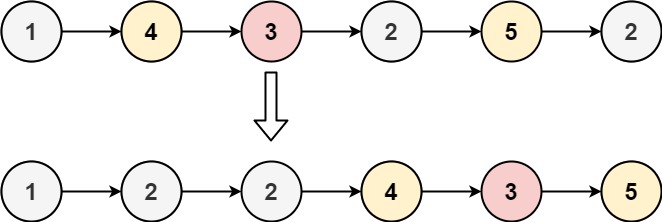
| Input: head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3
Output: [1,2,2,4,3,5]
|
Example 2:
1
2
| Input: head = [2,1], x = 2
Output: [1,2]
|
题目大意
给定链表的头节点 head 和一个值 x,要求将链表分隔成两部分:所有值小于 x 的节点排在所有值大于或等于 x 的节点之前。同时需要保留两部分中节点的原始相对顺序。
解题思路
可以通过构建两个临时链表来解决:
- 创建两个虚拟头节点,分别用于存储 "小于 x 的节点" 和 "大于等于 x 的节点"
- 遍历原链表,将每个节点分配到对应的临时链表中
- 最后将两个临时链表连接起来,前半部分的尾节点连接到后半部分的头节点
这种方法可以保证原始相对顺序不变,且只需一次遍历。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
// 创建两个虚拟头节点,分别用于存储小于x和大于等于x的节点
ListNode* dummyLess = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* dummyGreater = new ListNode(0);
// 用于构建两个链表的尾指针
ListNode* lessTail = dummyLess;
ListNode* greaterTail = dummyGreater;
// 遍历原链表
ListNode* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
if (current->val < x) {
// 加入到小于x的链表
lessTail->next = current;
lessTail = lessTail->next;
} else {
// 加入到大于等于x的链表
greaterTail->next = current;
greaterTail = greaterTail->next;
}
current = current->next;
}
// 将两个链表连接起来:小于x的链表尾部连接到大于等于x的链表头部
lessTail->next = dummyGreater->next;
// 确保新链表的尾部指向null
greaterTail->next = nullptr;
// 保存结果头节点并释放虚拟节点
ListNode* result = dummyLess->next;
delete dummyLess;
delete dummyGreater;
return result;
}
};
|
解法2:只修改值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
if (head == nullptr) return nullptr;
// 收集所有节点的值
vector<int> values;
ListNode* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
values.push_back(current->val);
current = current->next;
}
// 分离小于x和大于等于x的值,保持各自的相对顺序
vector<int> less, greater;
for (int val : values) {
if (val < x) {
less.push_back(val);
} else {
greater.push_back(val);
}
}
// 合并两个向量,小于x的在前,大于等于x的在后
vector<int> result;
result.insert(result.end(), less.begin(), less.end());
result.insert(result.end(), greater.begin(), greater.end());
// 将合并后的值重新赋给原链表节点(不改变节点位置)
current = head;
int i = 0;
while (current != nullptr) {
current->val = result[i++];
current = current->next;
}
return head;
}
};
|
- 收集值:先遍历链表,收集所有节点的值到一个向量中
- 分离值:将收集到的值分为 "小于 x" 和 "大于等于 x" 两部分,保持各自的相对顺序
- 合并值:将两部分值按顺序合并,小于 x 的在前,大于等于 x 的在后
- 重新赋值:将合并后的值按顺序重新赋给原链表的节点,节点位置保持不变


